How Startups Can Mitigate Cybersecurity Risks
By William R. Pardi
January 27, 2021
New tech startups are cropping up every day, leading the way with innovative technologies and beneficial applications and platforms. However, as these technologies grow, so do the methods of maliciously exploiting them, and according to this Medium article by Ryan McGheehan, startups must address and focus on security with the same intensity that they focus on growing and expanding their business. It can be a bit more complicated than just maintaining good password policy and load balancing your servers, and true peace of mind may require hiring dedicated security personnel and the help of other companies and startups.
According to an article by Forbes, there were over 3,800 data breaches in 2019, including three of the ten largest breaches in history. This figure shouldn’t be surprising, as technology is working its way into every facet of our lives, which increases attack vectors for malicious hackers along the way. For any startup and any technology, security can no longer just be a bonus or a selling point. It’s an absolute necessity.
However, startups already have enough on their plate, trying to keep costs down and allowing profit for growth. Many aspects of security simply boil down to maintaining proper etiquette in the development of applications, which will be covered more in depth later in the article, and training staff. Indeed, the best place to start is with mandatory cybersecurity education for all staff. All employees should be provided with training on how to avoid common cybersecurity risks and social engineering attacks.

Source
This information should be given to everyone in an organization no matter how distantly related their tasks or roles are to any major infrastructure. This is due to something called privilege escalation. Privilege escalation means that if an attacker can compromise one employee or system, they can elevate their privileges from there until they reach the system they want. It is equally important to educate your users on basic cybersecurity as well, such as never sharing their password to anyone. However, even with good employee and user education, and with any security mitigation in general, the threat will never be fully eliminated, meaning security precautions need to be taken a step further.
This means you need to think about securing the front end of your platform, service, or application. There are a variety of attacks that can be perpetrated via the public facing UI of your products, ranging from SQL injection attacks and cross-site scripting to password brute-forcing. As mentioned before, many of these cases are going to require educating software developers on good security etiquette, particularly coding security. For example, to mitigate attacks such as SQL injection or buffer overflow, a developer would implement input validation, implementing code in a function that checks for SQL syntax or invalid inputs and preventing malicious code entered by an attacker from interfering with the web applications database.
Input validation is an effective way to counter many different kinds of client-side exploits, including cross-site scripting and XML injection, but another common and very potent flaw left behind by developers is the improper management of ‘backdoors’. A backdoor within software is incredibly useful for authorized developers and administrators to quickly gain high level access to the application in order to make fundamental changes to the service without pulling the platform from production. However, if these backdoors are not protected or are mismanaged, it may be fairly easy for an attacker to quickly gain root level access to the system and make their own sweeping changes that suit their needs.
While gaining troves of valuable information with the aforementioned methods is the goal of many attackers, some don’t bother ever touching your application or service. Instead, they may use attacks such as posing as a middleman between you and your client, or stealing packets from customers as they browse your website using something such as Wireshark, compromising the confidentiality of transmitted information. Hence, any modern dynamic website needs to be protected with TLS, as SSL is now considered outdated, and remote employees connecting to sensitive services within the organization must use a reputable VPN. Countless exploits and tools exist for the sake of stealing information in transit, which is why HTTP won’t cut it for any dynamic web service.
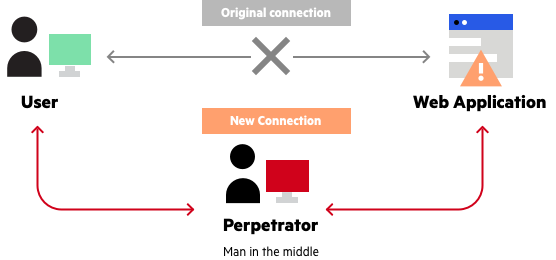
Source
Many attackers don’t need any information at all and instead simply want to compromise your company’s availability to customers through DoS (Denial of Service) attacks. This is generally accomplished by flooding your servers with invalid connection requests that consume resources until your service can no longer acknowledge legitimate requests from customers, or in worse cases, cause the server to crash altogether. This attack is most commonly mitigated using load balancers and backup servers.
Malware is another huge concern, as there are many varieties that can potentially cause immense damage to your organization, such as large scale data breaches that result in excess of millions of dollars in recovery costs. They can be transmitted in many different ways, ranging from drive-by links as mentioned before, to disgruntled employees seeking vengeance for a perceived injustice and uploading malware from inside the organization. If some types of malware manage to successfully exploit a machine or infiltrate the network, they may remain undetected for weeks or months, and when they are found, they can be very difficult to remove.

Source
One mitigation for this threat is a reliable antivirus. This may seem like a no brainer, but even with antivirus solutions, they can’t be just installed and forgotten about, endowing you with a false sense of security. Risks are never completely eliminated, and in order to mitigate risks as much as possible, antivirus software and solutions need to be properly configured, such as scheduling regular, full scans of the system they’re installed on.
There are countless security risks and an equal number of threats poised to exploit them, and the ones listed have been just a small sample of some of the most common varieties. For a small startup, it may seem daunting to tackle this challenge, which is why it is better to outsource certain tasks to other entities in order to transfer the risks to an organization better suited to handle them. This goes beyond just purchasing insurance, and while many services have their costs, it will generally be cheaper than hiring a team of security professionals to constantly monitor and lock down your systems.
For example, it is already common knowledge for nearly any business to use an external antivirus software rather than develop their own. This principle can be extended to other services, such as web hosting. Particularly for startups, hosting your platform on your own server may seem enticing to avoid paying fees to another company to host it for you, but when you factor in the costs of load balancers to mitigate DoS attacks or other security costs (most of which are taken care of by the hosting company) you can save yourself time, money, and a huge headache.
Outsourcing login solutions can also save time and money while protecting your company and your clients. Aside from the inherent risks of passwords and password management (which we’ve covered in another article), there is the security of the front end of your application that needs to be considered as well to avoid risks such as code injection attacks. Relying on another startup such as humanID to provide your login solution is a better option. humanID utilizes user’s phone numbers to provide a secure and anonymous login, with no need for you to host a database that needs to be locked down or create a web application that can be exploited and would need immediate attention to security.
Technology has made it much easier for any startup to make themselves known, but with these new capabilities come new risks. In order to provide customers with confidence and to protect their well-being, your platform needs to be secure and protected from a growing number of threats in the digital realm. Tackling these threats is a daunting and potentially impossible task to handle on your own, which is why the solution may be to contract with other entities, such as humanID, to handle certain aspects of your technological infrastructure for you.
